How do you treat an inflamed vein?
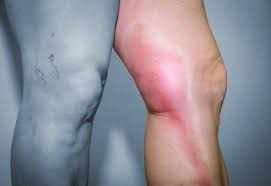
Superficial vein inflammation, also known as superficial thrombophlebitis or phlebitis, is a condition where a superficial vein close to the surface of the skin becomes inflamed and may develop a blood clot (thrombus). This condition can occur spontaneously or as a result of trauma to the vein, and while usually not life-threatening, it can cause discomfort and complications if left untreated. Lioton gel is used for local treatment of inflammation of superficial veins and haematomas.
Understanding Superficial Vein Inflammation:
Causes and Risk Factors:
Superficial vein inflammation typically arises from one or more of the following factors:
- Trauma or Injury: Direct injury to a vein, such as from intravenous (IV) catheters, injections, or physical trauma, can trigger inflammation and clot formation.
- Infection: In rare cases, an infection in a superficial vein can cause inflammation and lead to thrombophlebitis. Also try Heparin gel.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions that increase the risk of blood clotting, such as varicose veins, obesity, pregnancy, and certain autoimmune disorders, can predispose individuals to superficial vein inflammation.
- Inactivity: Prolonged periods of immobility or sedentary behavior, such as during long flights or bed rest after surgery, can contribute to sluggish blood flow and increase the risk of clot formation.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of superficial vein inflammation can vary depending on the severity and location of the affected vein, but commonly include:
- Redness: The skin over the affected vein may appear red or warm to the touch.
- Pain or Tenderness: Pain or tenderness along the course of the vein, especially when touched or pressed.
- Swelling: Swelling or lumpiness along the vein, indicating inflammation and possible clot formation.
- Palpable Cord: In some cases, a firm, palpable cord may be felt under the skin along the inflamed vein.
- Fever: If an infection is present, fever and chills may accompany the inflammation.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing superficial vein inflammation typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider to assess the symptoms and location of the inflammation. Additional tests may include:
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound scan can confirm the presence of a blood clot (thrombus) in the affected vein and help determine the extent of the inflammation.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess clotting factors and rule out underlying conditions that contribute to clot formation.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for superficial vein inflammation focuses on relieving symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Depending on the severity and underlying cause, treatment options may include:
1. Self-Care Measures:
- Compression: Wearing compression stockings or bandages can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow in the affected vein.
- Elevation: Elevating the affected limb above heart level when resting can also help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can alleviate pain and promote circulation.
2. Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Anticoagulants: In some cases, especially if there is a significant clot or risk of extension, your doctor may prescribe anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) to prevent clotting and reduce the risk of complications.
3. Medical Procedures:
- Vein Removal: If the inflammation and clotting recur frequently or are severe, the affected vein may need to be surgically removed (phlebectomy) or treated with minimally invasive techniques such as sclerotherapy.
- Thrombectomy: In cases where there is a large or painful clot, a procedure called thrombectomy may be performed to remove the clot and alleviate symptoms.
4. Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Varicose Veins: Treating underlying conditions such as varicose veins through lifestyle changes, compression therapy, or surgical interventions can reduce the risk of recurrent superficial vein inflammation.
5. Follow-up and Monitoring:
- Regular Monitoring: It’s essential to follow up with your healthcare provider to monitor the healing process, evaluate any recurrent symptoms, and adjust treatment as necessary.
Complications:
While superficial vein inflammation typically resolves with appropriate treatment and self-care measures, complications can occur in some cases:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): If a blood clot in a superficial vein extends into deeper veins, it can lead to DVT, a more serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A clot that breaks loose and travels to the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism, a life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical treatment.
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI): Recurrent or untreated superficial vein inflammation can lead to chronic venous insufficiency, characterized by leg swelling, skin changes, and ulcer formation.
Prevention:
Taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of superficial vein inflammation can help prevent recurrence and complications:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity promotes healthy blood circulation and reduces the risk of clot formation.
- Avoid Prolonged Immobility: If you must remain sedentary for long periods, take breaks to stretch and move your legs.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of vein inflammation and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of clotting.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Treat and manage conditions such as varicose veins or diabetes that contribute to vein inflammation.
Conclusion:
Superficial vein inflammation, while generally not life-threatening, can cause significant discomfort and lead to complications if untreated. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to relieve symptoms, prevent clotting complications, and promote healing. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies for superficial vein inflammation, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively and improve overall vein health. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is crucial to monitor progress and address any concerns promptly.