Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide by FlowCare
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This condition can lead to severe complications if not detected and treated promptly. Understanding the deep vein thrombosis symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. At FlowCare, we are committed to providing you with the knowledge and tools to recognize DVT symptoms and take appropriate action.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition in which blood clots form in the deep veins of the body. These clots can obstruct blood flow, leading to swelling, pain, and other complications. While DVT most commonly occurs in the legs, it can also develop in other parts of the body. Recognizing the symptoms early is essential for preventing further complications such as pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a blood clot travels to the lungs.
Common Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
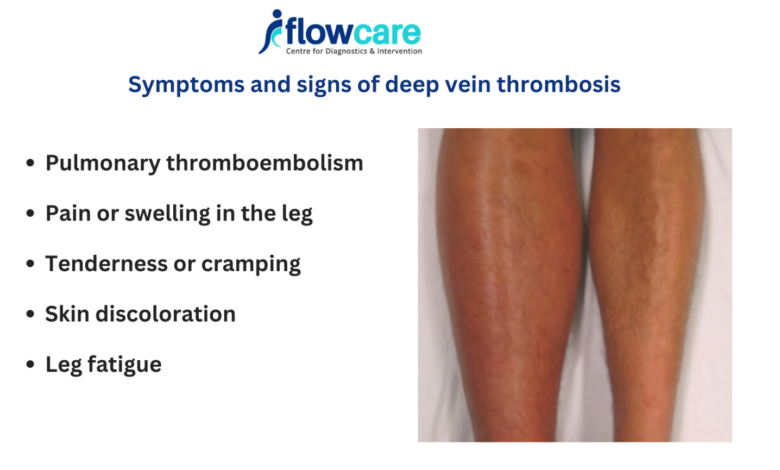
Recognizing deep vein thrombosis symptoms can be challenging because they can vary from person to person. However, there are several common symptoms to watch for:
Swelling
One of the most common symptoms of DVT is swelling in the affected leg. The swelling may occur suddenly or gradually and is often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness.
Pain
Pain or tenderness in the leg, especially when standing or walking, is another common symptom. The pain may feel like a cramp or soreness and is often located in the calf or thigh.
Red or Discolored Skin
The skin over the affected area may become red or take on a bluish tint. This discoloration is due to reduced blood flow and increased pressure in the veins.
Warmth
The affected area may feel warmer than the surrounding skin. This warmth is caused by inflammation and increased blood flow to the area.
Visible Veins
In some cases, the veins near the surface of the skin may become more visible. These veins may appear swollen and prominent.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the more common symptoms, there are several less common symptoms of deep vein thrombosis that individuals should be aware of:
Leg Fatigue
Some individuals with DVT may experience a feeling of fatigue or heaviness in the affected leg. This symptom can be subtle and easy to overlook.
Itching
The skin over the affected area may become itchy. This symptom is less common but can occur due to changes in blood flow and pressure in the veins.
Shortness of Breath
If a blood clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and a rapid heart rate. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Understanding the risk factors for DVT can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce their risk. Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing deep vein thrombosis:
Prolonged Inactivity
Sitting or lying down for extended periods, such as during long flights or bed rest, can increase the risk of DVT. This is because prolonged inactivity can lead to reduced blood flow and increased clot formation.
Surgery
Major surgeries, especially those involving the legs or hips, can increase the risk of DVT. Surgery can damage blood vessels and reduce mobility, both of which contribute to clot formation.
Injury
Trauma to the veins, such as fractures or severe muscle injuries, can increase the risk of DVT. This is because injury can damage blood vessels and lead to inflammation.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and inflammatory bowel disease, can increase the risk of DVT. These conditions can cause changes in blood flow and increase the likelihood of clot formation.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy increases the risk of DVT due to hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins in the legs. The risk is highest during the third trimester and the first six weeks postpartum.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy and birth control pills can increase the risk of DVT. These medications can cause changes in blood clotting and increase the likelihood of clot formation.
Genetics
A family history of DVT or blood clotting disorders can increase the risk of developing the condition. Certain genetic factors can make individuals more prone to clot formation.
Prevention and Management of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Preventing and managing deep vein thrombosis involves several strategies. At FlowCare, we recommend the following steps to reduce the risk of DVT and manage symptoms effectively:
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is essential for promoting healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of DVT. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of DVT. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce this risk.
Avoid Prolonged Inactivity
If you need to sit or lie down for extended periods, make sure to take breaks to move around and stretch your legs. This can help promote healthy blood flow and reduce the risk of clot formation.
Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of DVT. These stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping to prevent blood from pooling and clotting.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help keep your blood thin and reduce the risk of clot formation. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
Follow Medical Advice
If you have risk factors for DVT or have been diagnosed with the condition, it is essential to follow your healthcare provider’s advice. This may include taking medications to prevent or treat clots, attending regular check-ups, and making lifestyle changes to reduce your risk.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of deep vein thrombosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications such as pulmonary embolism. If you experience sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or a rapid heart rate, seek emergency medical care immediately, as these may be signs of a pulmonary embolism.
FlowCare: Your Partner in Vascular Health
At FlowCare, we are dedicated to helping you understand and manage deep vein thrombosis symptoms. Our team of experts is here to provide you with the information and support you need to stay healthy and prevent complications. Whether you are looking for advice on preventing DVT or need treatment for an existing condition, FlowCare is here to help.
Conclusion
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and management. By understanding the symptoms and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. At FlowCare, we are committed to helping you stay informed and take control of your vascular health. If you have any concerns or need assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team. Your health is our priority, and we are here to support you every step of the way.